Individuals with alcohol use disorder can develop severe health issues like inflammation of the liver. Alcoholic hepatitis is one stage away from irreversible liver damage. While the first part of treatment is to stop drinking, there are additional steps you can take for recovery.
Alcohol use is ingrained in our society and culture. However, there’s a dark side to this substance. For individuals living with alcoholism, their addiction creates chaos for them and their loved ones.
Many individuals who suffer from alcohol use disorder sacrifice their health, experiencing issues such as inflammation of the liver. Alcoholic hepatitis is a severe condition that develops because of chronic alcohol abuse.
After years of heavy alcohol use, the liver becomes inflamed, significantly increasing one’s risk of potentially life-threatening complications. Treatment options are available, and the first step is to quit drinking alcohol.

What is Alcoholic Hepatitis?
Alcoholic hepatitis is a severe condition related to alcoholic liver disease. It’s part of a process that eventually involves cirrhosis, which is scarring of the liver. (1)
This condition is often referred to as “end-stage” liver disease, as it occurs after the development of alcoholic hepatitis. Once your liver cells become damaged, the progression can be quick if you do not achieve abstinence. (1) (2)
The stages of liver disease are as follows:
- Fatty liver disease
- Alcoholic hepatitis
- Cirrhosis
Since hepatitis is associated with excessive, long-term alcohol consumption, quitting drinking is the only true preventive measure.
If you currently have fatty liver disease, seeking help for alcoholism could help you prevent alcoholic hepatitis. If you have been diagnosed with alcoholic hepatitis, taking action today will help you stop the progression to cirrhosis.
The effects of alcoholic hepatitis can be reversed, but once your liver has scar tissue, that damage is permanent. You may require a liver transplant if your liver function becomes too poor. That is why it’s crucial to seek help as soon as possible.
Causes and Risk Factors of Alcohol-Induced Hepatitis
Alcohol-induced hepatitis is a liver inflammation resulting from excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption. (3) The liver, a vital organ for metabolism and detoxification, becomes susceptible to damage due to alcohol’s toxic effects.
The primary cause of alcohol-induced hepatitis is the toxicity of ethanol, a substance found in alcoholic beverages. When the liver metabolizes alcohol, it produces harmful byproducts that trigger inflammation, leading to hepatitis.
Chronic alcohol abuse overwhelms the liver’s ability to detoxify, causing persistent inflammation and damage. This means that large amounts of alcohol can have detrimental effects on the body.
Risk Factors: Several factors contribute to the risk of developing alcohol-induced hepatitis: (4)
- Amount and Duration of Alcohol Consumption: The risk increases with higher alcohol intake over an extended period. Daily heavy drinking or binge drinking sessions raise the likelihood of liver damage.
- Individual Susceptibility: Genetic factors play a role in how individuals metabolize alcohol. Some people are more genetically predisposed to liver damage from alcohol than others, especially if there is a history of chronic liver disease in the family. (5)
- Nutritional Status: Poor nutrition, common in individuals with alcohol use disorder, can exacerbate liver damage. Malnutrition weakens the liver’s ability to regenerate and repair itself.
- Gender and Age: Women are generally more susceptible to alcohol-induced liver damage than men. Older age also increases vulnerability, as the liver’s resilience diminishes with age.
Prevention: Preventing alcohol-induced hepatitis involves reducing or eliminating alcohol consumption. Individuals at risk should seek support for alcohol cessation, adopt a balanced diet, and address nutritional deficiencies.
Regular medical check-ups and early intervention for alcohol-related issues can significantly reduce the risk of developing this serious liver condition.
Symptoms of Alcoholic Hepatitis
There is not one defining symptom that signifies alcoholic hepatitis. This condition can cause a range of symptoms for heavy drinkers, including the following:
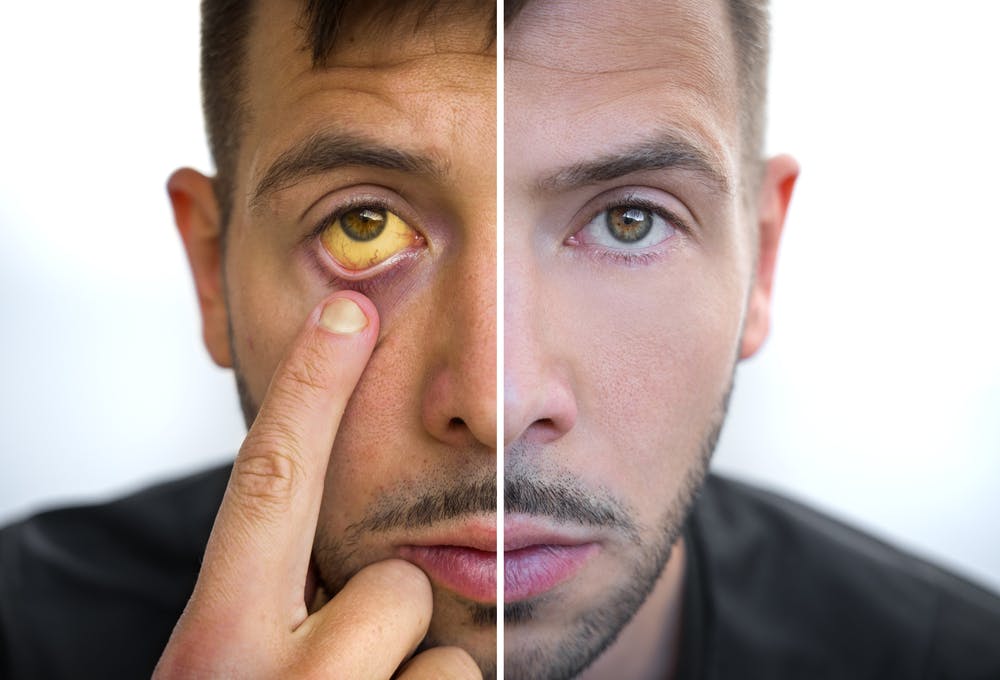
- Clinical jaundice is present in the majority of cases, which causes a yellowing of the skin and the white areas of your eyes short term. (6)
- When blood tests are administered, nearly every patient will have too much bilirubin, a substance created when red blood cells break down.
- Patients may experience upper abdominal pain and a tender, enlarged liver.
- It’s not uncommon to have a heart rate above 100 beats a minute, which may be discovered during a routine examination.
- A fever can develop. However, this symptom can also indicate an infection or liver cancer.
Many patients develop liver cirrhosis if heavy drinking continues, so symptoms of this condition could be present. The features range from bleeding in your stomach to small or purple marks on your skin. Another common symptom is ascites, a fluid buildup in your stomach area.
If you have a mild case of alcoholic hepatitis, you may not have any symptoms. However, as the damage to your liver worsens, you may begin to notice changes in your appetite. Many patients fail to recognize the severity of the situation.
Complications of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis, if left untreated or not managed effectively, can lead to severe complications, significantly impacting liver health. The following are potential complications associated with alcoholic hepatitis:
- Cirrhosis: Prolonged and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to the development of cirrhosis, a late-stage scarring of the liver tissue. Cirrhosis impairs liver function and can lead to irreversible damage. (7) It poses a heightened risk of liver failure and complications like portal hypertension and esophageal varices.
- Liver Failure: As alcoholic hepatitis progresses, the liver’s ability to perform essential functions diminishes, potentially culminating in liver failure. Liver failure is a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention. Symptoms may include confusion, jaundice, bleeding disorders, and fluid retention.
- Hepatic Encephalopathy: Advanced liver disease, including alcoholic hepatitis, may result in hepatic encephalopathy. This condition involves cognitive impairment due to the liver’s inability to filter toxins effectively. Symptoms range from mild confusion to severe neurological dysfunction, impacting overall mental function. (8)
- Ascites: Alcoholic hepatitis can lead to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, a condition known as ascites. This fluid buildup results from increased pressure in the portal vein and impaired liver function. Ascites cause abdominal swelling, discomfort, and difficulty breathing. (9)
- Kidney Dysfunction: Complications associated with alcoholic hepatitis can extend to kidney function. Hepatorenal syndrome, a condition characterized by impaired kidney function due to liver disease, may develop, exacerbating overall health challenges.
- Increased Risk of Infections: Weakened immune function resulting from alcoholic hepatitis increases susceptibility to infections. Bacterial peritonitis, a serious infection of the abdominal lining, is a potential complication, further compromising health.
Diagnosis of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Accurate and timely diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis is crucial for implementing appropriate treatment strategies. Various diagnostic methods are employed to assess liver function and identify the presence of alcoholic hepatitis:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests, including liver function tests and markers such as elevated liver enzymes, bilirubin, and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), help evaluate the extent of liver damage and inflammation. (10)
- Imaging Tests: Imaging studies, such as ultrasound, CT scan, and MRI, provide visual insights into the liver’s condition. These tests can reveal signs of inflammation, fatty deposits, or cirrhosis.
- Liver Biopsy: A liver biopsy is what happens when medical staff obtain a small sample of liver tissue for microscopic examination. This procedure will confirm the presence of alcoholic hepatitis. It can also assess the severity of liver damage, and guide treatment decisions. (11)
- Clinical Assessment: Medical professionals conduct a comprehensive clinical assessment, considering symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle factors to make an accurate diagnosis. This approach will make sure that they have a thorough understanding of the individual’s health status for better treatment.
By employing these diagnostic methods, healthcare providers can precisely identify alcoholic hepatitis, assess its severity, and tailor treatment plans to address the specific needs of the individual. Early and accurate diagnosis enhances the chances of successful intervention and improved outcomes.
Treatment Options for Alcoholic Hepatitis
Technically, there is no one-size-fits-all cure for alcoholic hepatitis. Many options have been researched over the years, including corticosteroids. Clinical trials show these anti-inflammatory medications can reduce the risk of death within 28 days for patients with severe cases. (12)
If you have mild alcoholic hepatitis, it is often reversible. The catch to this healing process is that you must stop drinking permanently. If your symptoms are not too advanced, taking steps to quit drinking can help your liver recover.
No magic treatment works for everyone, as each individual is unique concerning the severity of their condition, history of abuse, medical history, etc. However, research shows that the following treatments can help treat alcoholic hepatitis. (13)
- Optimal nutrition — Alcohol use disorders cause significant malnutrition and deficiencies in vitamins, minerals, and protein. Your building requires these nutrients to heal. Foods to include in your diet include beets, avocados, bananas, barley, figs, etc. Your diet plan is something you can discuss with your healthcare team.
- Antioxidant therapy — Related to nutrition, it is recommended that you consume more antioxidants to help reduce the inflammatory response. Opt for plenty of dark leafy greens, squash, berries, sweet potatoes, etc. You can also take supplements.
- Complete abstinence — Most physicians will refer patients to an addiction specialist. The longer you wait to start treatment, the more severe alcoholic hepatitis will become, increasing your risk of immediate liver failure. If you are living with a co-occurring mental health condition, a professional treatment facility will help you address any underlying concerns that may impact your recovery.
Alcoholic Hepatitis Prevention Strategies
Preventing alcoholic hepatitis is crucial for maintaining liver health and overall well-being. Here are key strategies, particularly beneficial for those at risk or in the early stages of liver disease:
- Abstinence from Alcohol: The most effective prevention measure is to cease alcohol consumption entirely. For those at risk or diagnosed with alcoholic hepatitis, stopping alcohol intake is paramount. This step allows the liver to recover and reduces the risk of further damage.
- Seek Professional Help: Individuals struggling with alcohol dependence should seek professional assistance. Alcohol cessation programs, counseling, and support groups can provide guidance and motivation for sustained abstinence. Healthcare professionals can tailor treatment plans to individual needs.
- Nutritional Support: Proper nutrition supports liver regeneration and helps combat the effects of malnutrition associated with alcohol abuse. A diet that is rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants will be beneficial to overall liver function.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Routine medical check-ups are essential for early detection and monitoring of liver health. Regular blood tests and liver function assessments can identify potential issues before they progress to more severe conditions. Timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
- Vaccinations: Vaccinations against hepatitis A and B are recommended for individuals with alcoholic liver disease. These vaccinations prevent additional stress on the liver caused by viral infections, reducing the risk of complications.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is vital for liver health. Excess weight, especially abdominal fat, contributes to liver inflammation. Adopting a lifestyle that includes regular physical activity and a balanced diet helps manage weight and supports liver function.
- Monitor Medication Use: Some medications can exacerbate liver damage. Individuals with alcoholic hepatitis need to consult healthcare providers before taking any medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Medical professionals can recommend safe alternatives that do not harm the liver.
- Manage Coexisting Conditions: Individuals with alcoholic hepatitis often have co-existing health conditions. Managing conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and cholesterol levels can help your liver. By staying on top of these health issues, the burden your liver takes will be reduced.
Take the Next Steps for Health and Recovery
Seeking alcoholism treatment isn’t easy — it can be an overwhelming step. However, if you’re concerned about alcoholic hepatitis, taking this step could save your life.
If you or your loved one abuses alcohol and are concerned about alcohol-related liver disease, it’s time to seek the support of an experienced treatment center. Quitting drinking is a complex process that often requires a range of treatment options.
No two individuals are the same, so why should their treatment plans be identical?
Ready to change your life and actively improve your health? Today is the day to call Zinnia Health. We strive to heal our clients for good, helping them achieve a life they love, free from alcohol. Please contact our alcoholism hotline available 24 hours per day at (855) 430-9439 to discuss our detox, outpatient, and inpatient options — we’re here to help.
Citations
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470217/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5513682/
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/hepatitis/alcoholic-hepatitis
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/alcoholic-hepatitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20351388
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4056340/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544252/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/cirrhosis/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6668878/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470482/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482489/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10224864/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29738698/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5828019/
Related Articles
- Alcohol Addiction Treatments
- Can You Get Drunk Off Vanilla Extract? What Are The Risks?
- Is Alcoholism a Disease? Learn The Facts